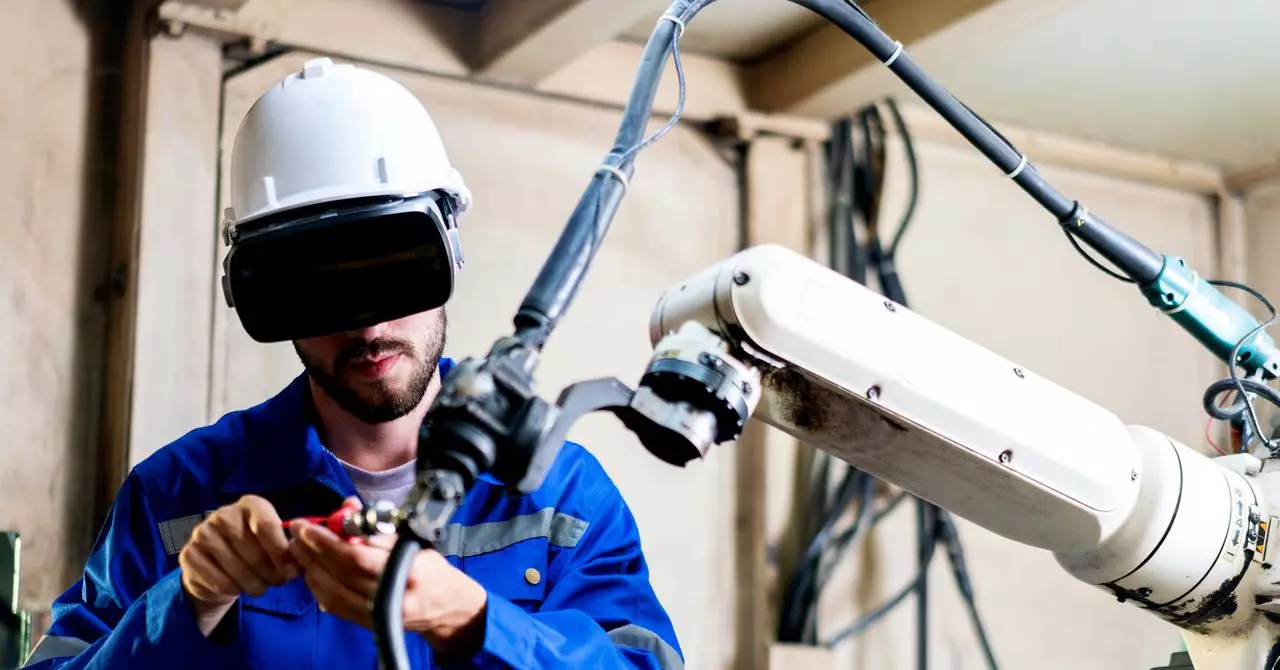
The landscape of manufacturing has been drastically transformed, not merely by the advancement of technology but by its ingenious integration into everyday processes. Traditionally, companies like BMW faced significant logistical challenges when refitting factories for new models, often requiring physical interventions to troubleshoot any potential issues in the production line. Nowadays, these time-consuming and resource-intensive methods are being replaced by revolutionary digital simulations. The advent of the industrial metaverse has emerged as a remarkable answer to the complexities that plagued manufacturing, ushering a new era where efficiency reigns supreme.
Instead of sending teams to troubleshoot and manually push chassis through production lines, manufacturers can now leverage sophisticated simulations. By employing a digital twin of their manufacturing facilities—a near-identical virtual replica—engineers can identify and resolve issues even before the inception of the physical production line. The shift from physical trials to digital testing not only hastens the production process but also conserves substantial time and financial resources for manufacturers, leading to an unprecedented acceleration of innovation.
The Rise of the Industrial Metaverse
The term “metaverse,” initially popularized in the context of virtual social interactions through avatars, has remarkably found renewed purpose in the industrial realm. It transcends mere virtual meetings or online games, becoming a game-changer for sectors reliant on complex manufacturing workflows. Experts anticipate that the industrial metaverse could surge in worth to $100 billion globally by 2030, a recognition underscored by the World Economic Forum’s insights.
The industrial metaverse is a powerful convergence of technologies: augmented reality (AR), simulations, and sophisticated sensors synced harmoniously to create a seamless manufacturing workflow. Varvn Aryacetas of Deloitte coins it as “spatial computing,” emphasizing its potential to blend physical and digital environments to elevate productivity across industries.
Innovative Applications Across Industries
A compelling illustration of the metaverse’s capabilities is evident in major players like Nvidia, a titan in AI and graphics technology. The unveiling of Nvidia’s Omniverse platform introduces a robust suite of tools destined to reshape manufacturing processes. It lays the groundwork for creating simulations, generating digital twins, and driving automation, thus acting as a backbone for the industrial metaverse.
The implications of this technology are monumental. Take Lowe’s, the home improvement giant, which utilizes Omniverse to refine store layouts virtually before transitioning changes into physical locations. This proactive methodology not only minimizes disruption during renovations but also optimizes the customer experience—a hallmark of modern retail strategy. Similarly, Zaha Hadid Architects harnesses the capabilities of the industrial metaverse to foster collaboration on projects in a completely virtual environment, paving the way for ingenious designs that can be explored remotely.
Amazon capitalizes on simulation technology to train robotic systems effectively before they are deployed in warehouses, ensuring that operations run like clockwork. BMW stands at the forefront, employing virtual models to simulate its entire manufacturing process—right from the assembly line to the projected human resources involved. This innovative approach empowers BMW to create error-free models for factories before any brick is laid, ultimately leading to optimized operational efficiencies.
The Technical Backbone of Innovation
The foundation of this impressive digital transformation lies within the infrastructure that enables such sophisticated modeling. BMW’s adaptation of Universal Scene Description (OpenUSD), originally conceived by Pixar, exemplifies a commitment to technological innovation that spans well beyond the automotive industry. This open-source format, combined with Omniverse’s technical prowess, empowers manufacturers to create intricate and interactive models of their facilities, thus revolutionizing how production lines are conceptualized and constructed.
The complexity of a virtual factory can be astounding, with the space needing to be navigable just like the physical equivalent. BMW has ingeniously style-mixed gaming techniques with practical applications, evolving from gaming-style navigation to more intuitive interfaces reminiscent of Google Street View. By doing so, they ensure accessibility for all users, not just technologically inclined engineers.
As the industrial metaverse continues to evolve, the question remains: what boundaries will it shatter next? We are witnessing a critical point in manufacturing, where the integration of advanced digital tools will redefine the entire industry, unleashing creativity, and efficiency in previously unimaginable ways.