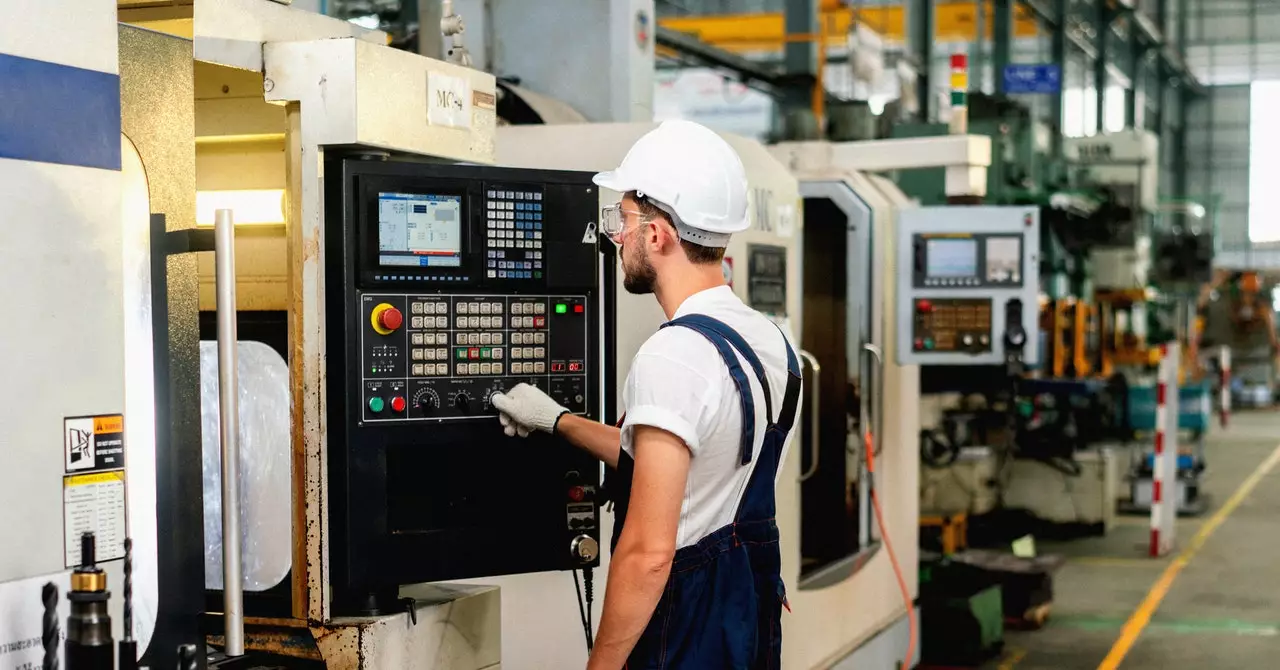
The manufacturing landscape has undergone a monumental transformation since the turn of the 20th century. One particular component, the steel ball bearing, has seen its grinding machinery remain relatively unchanged since approximately 1900. The essence of this machinery still revolves around grinding precision, but the environment surrounding it has dramatically evolved. Innovations in automation and connected technologies have revolutionized how manufacturers optimize production lines, making processes not just faster but also more efficient and less reliant on human intervention. The initial steps of steel ball production involve cutting steel wire, which is then molded into rough spheres and subjected to a rigorous series of hardening and grinding processes. It is within these grinding processes that precision becomes paramount; the finished products must meet stringent requirements, achieving roundness within a tenth of a micron.
The Allure of Automation in Manufacturing
The journey toward automation in manufacturing has positioned human operators to take on more analytical roles. As production lines become increasingly autonomous, the pressing task for workers is to identify anomalies early in the process. Automated machinery, complemented by conveyor systems, slashes production time without compromising quality. However, as industry moves toward the adoption of artificial intelligence, ongoing human oversight remains vital, especially in diagnosing the underlying issues causing production setbacks.
In facilities like Schaeffler’s Hamburg plant, the intricacies of ball bearing production create a highly detailed web of processes, where even the slightest defect can halt progress. However, when defects crop up, the root cause often eludes quick identification. The search could point to an incorrectly calibrated tool or a malfunctioning grinding wheel. Thus, detecting these problems translates into a complex crossword puzzle in which multiple pieces of industrial equipment must be analyzed.
To address such challenges, Schaeffler recently adopted Microsoft’s Factory Operations Agent—a groundbreaking step in utilizing AI in manufacturing. This product, which operates similarly to conversational AI models, represents a significant leap in how factories address defects, machine Downtime, and inefficient energy consumption. Companies have begun to realize the value of harnessing data for operational insight, and this integration of AI is enabling them to do just that.
Described as a “reasoning agent,” the Factory Operations Agent leverages vast amounts of manufacturing data to provide accurate and timely answers to operational queries. The beauty of this solution is the ease with which it can respond to questions like, “What accounts for the spike in defects?” The agent links various data points across the manufacturing process to help detect issues with remarkable clarity. However, what stands out about this technology is not merely the chatbot-like interface but its integration within an existing ecosystem of data analytics.
Schaeffler’s implementation underscores the immense potential found in data-driven decision-making. This translates to more than just an advanced AI tool—it symbolizes the convergence of operational technology with smart data platforms like Microsoft Fabric. With expansive data at their fingertips, manufacturers can optimize plant operations on a global scale. This enables stakeholders to make well-informed decisions that drive efficiency, enhancing their competitive position in the market.
Despite the sophistication of this AI system, it is crucial to understand the limitations at play. The Factory Operations Agent functions as a data access tool rather than an independent decision-maker. It remains a supportive entity focused on answering queries rather than executing autonomous decisions, empowering employees to navigate the manufacturing landscape more effectively.
In essence, the manufacturing journey for products like steel ball bearings is no longer solely reliant on mechanical precision; it is heavily intertwined with the innovations brought forth by automation and artificial intelligence. As factories continue to adapt with technology, the combination of human expertise and machine intelligence appears to be the way forward. This paradigm shift promises to enhance not merely productivity but operational intelligence, ultimately allowing manufacturers to embrace new opportunities in a rapidly changing world. The evolution of traditional processes into a seamlessly integrated smart manufacturing ecosystem heralds a new era of efficiency and precision—one that industry leaders must embrace to thrive in the competitive landscape of the future.