In our increasingly interconnected world, the efficiency of navigation and positioning systems such as the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) has become indispensable. GNSS, utilizing a constellation of satellites orbiting the Earth, has enabled everything from everyday smartphone apps to complex military operations. Despite its critical role, the reliability of GNSS signals faces escalating vulnerabilities due to potential jamming and spoofing efforts. These tactics—where false signals are emitted to mislead navigation—have been documented in various global hotspots including the South China Sea and conflict zones in Ukraine and the Middle East.
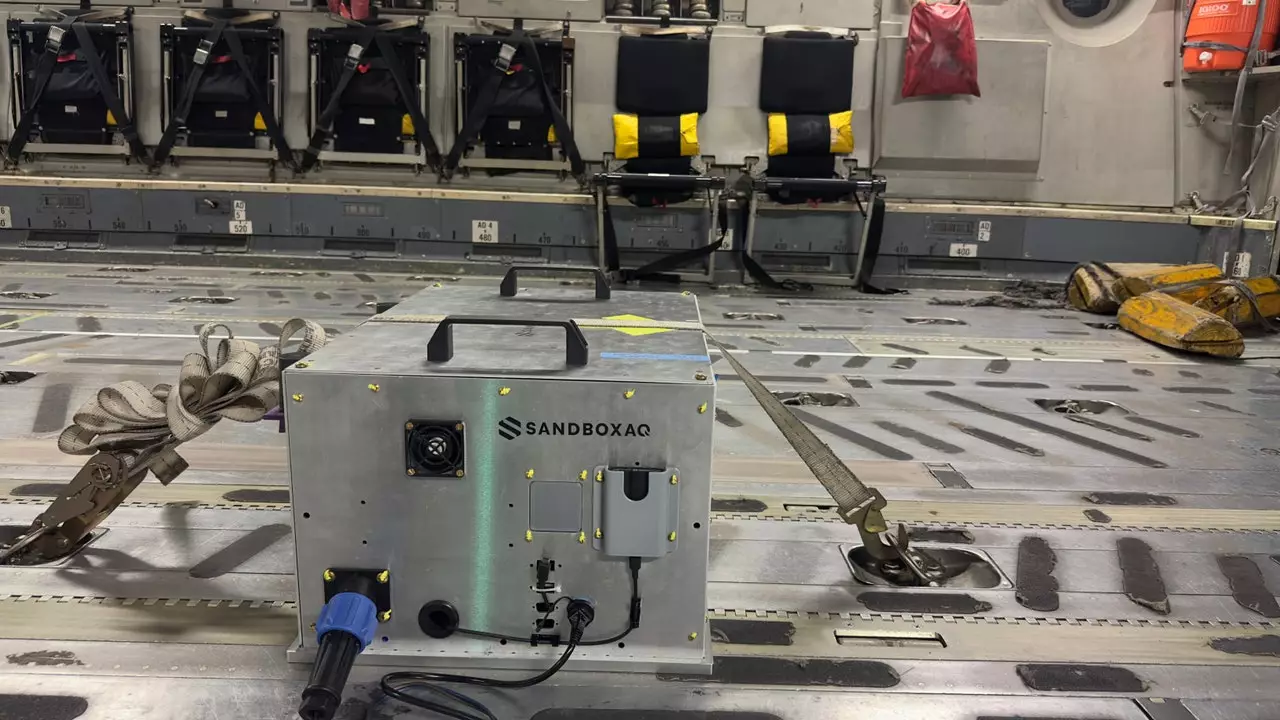
In response to these growing challenges, innovative solutions are emerging, among which SandboxAQ’s AQNav stands out. By integrating artificial intelligence with an alternative navigation method that taps into the Earth’s magnetic field, known as MagNav, this technology promises to enhance existing GNSS frameworks. This hybrid approach doesn’t seek to eliminate GNSS reliance but rather to bolster navigation systems for safety and resilience. According to Luca Ferrara, the general manager overseeing SandboxAQ’s navigation division, the technology acts as a supplementary layer that could serve as a primary navigation source during GPS outages or interferences.
Harnessing Quantum Magnetometers
At the heart of AQNav lies quantum magnetometers—highly advanced instruments capable of detecting minute changes in magnetic fields through the observation of subatomic particles. The sophisticated methodology involves identifying distinct magnetic signatures from geological formations underneath the Earth’s surface, a process referred to as acquiring the Earth’s “fingerprint.” With the guidance of artificial intelligence, the system can distinguish and mitigate external interferences in aircraft positioning, allowing for accurate navigation even when traditional GPS signals are compromised.
The practical implications of AQNav have not gone unnoticed. Since its inception, notable organizations like the US Air Force, Boeing, and Airbus have engaged in test flights to evaluate its effectiveness. Since May 2023, the system has been iterated and tested extensively under varied conditions, covering hundreds of kilometers across multiple aircraft types, including military transports and small single-engine planes. Such applications have demonstrated the technology’s adaptability and robustness in real-time scenarios, even amidst significant military exercises conducted by the US Air Force.
The brains behind SandboxAQ’s transformative navigation technology can trace their roots back to Google’s parent company, Alphabet. The concept was birthed within the innovative environment of its moonshot factory, focusing on practical applications for both artificial intelligence and quantum technology. This history not only illustrates the evolution of the technology but also highlights the potential for groundbreaking advancements in fields beyond navigation.
As reliance on satellite systems becomes ever more complex, the integration of disruptive technologies like AQNav could define the future of navigation. By addressing inherent weaknesses in GNSS while fortifying foundational systems, SandboxAQ embodies the potential to navigate not just through space, but also through the intricate web of challenges that modern technology presents.